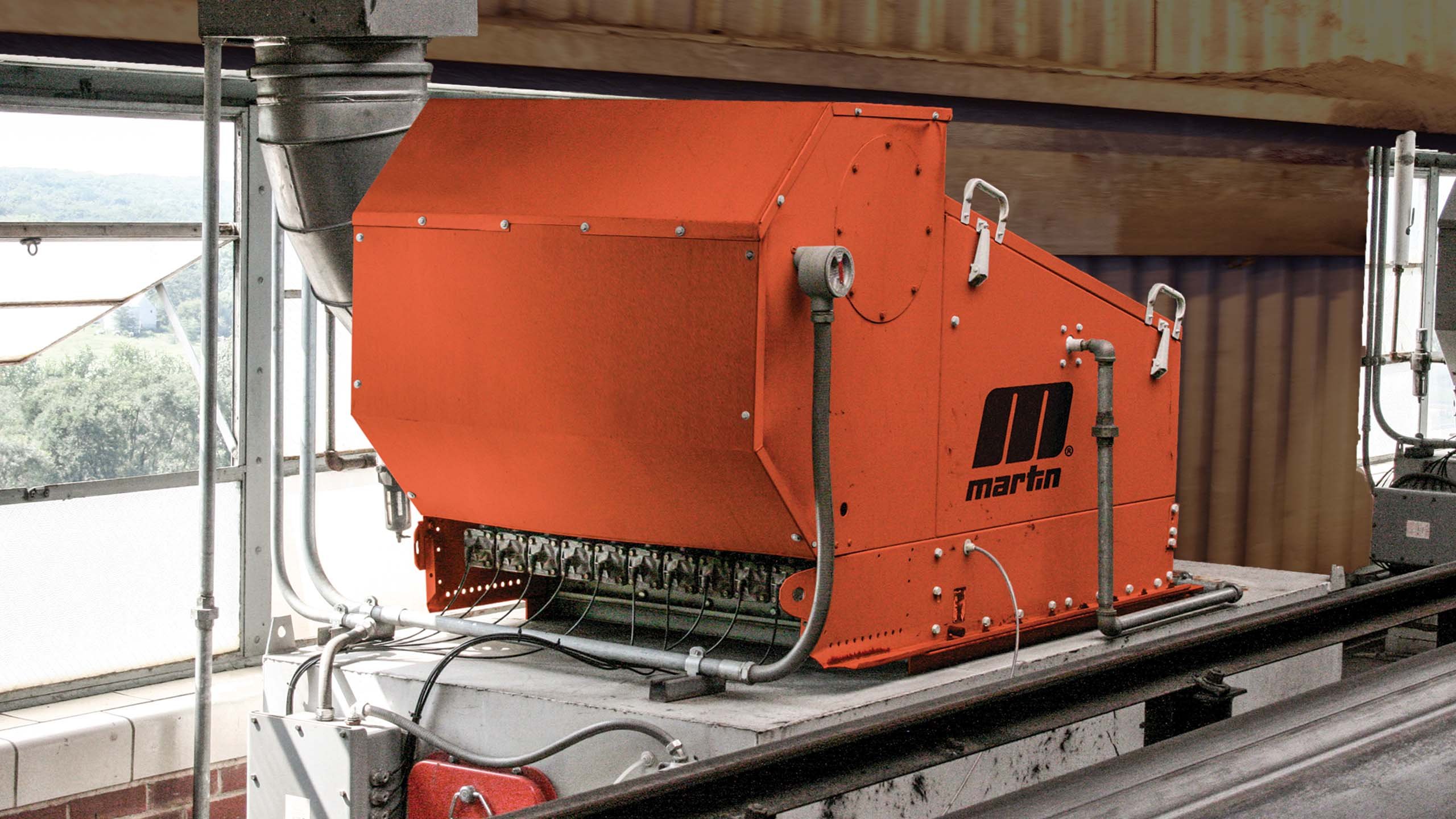
An extension of the unit concept is the insertable system, in which the dust collection system is incorporated within the dust-generation point itself. The filter is built into the enclosure around the dust-creation point, with the aim of controlling the dust at its source. The dust is not “extracted;” it is collected and periodically discharged back into the material stream within the enclosure.
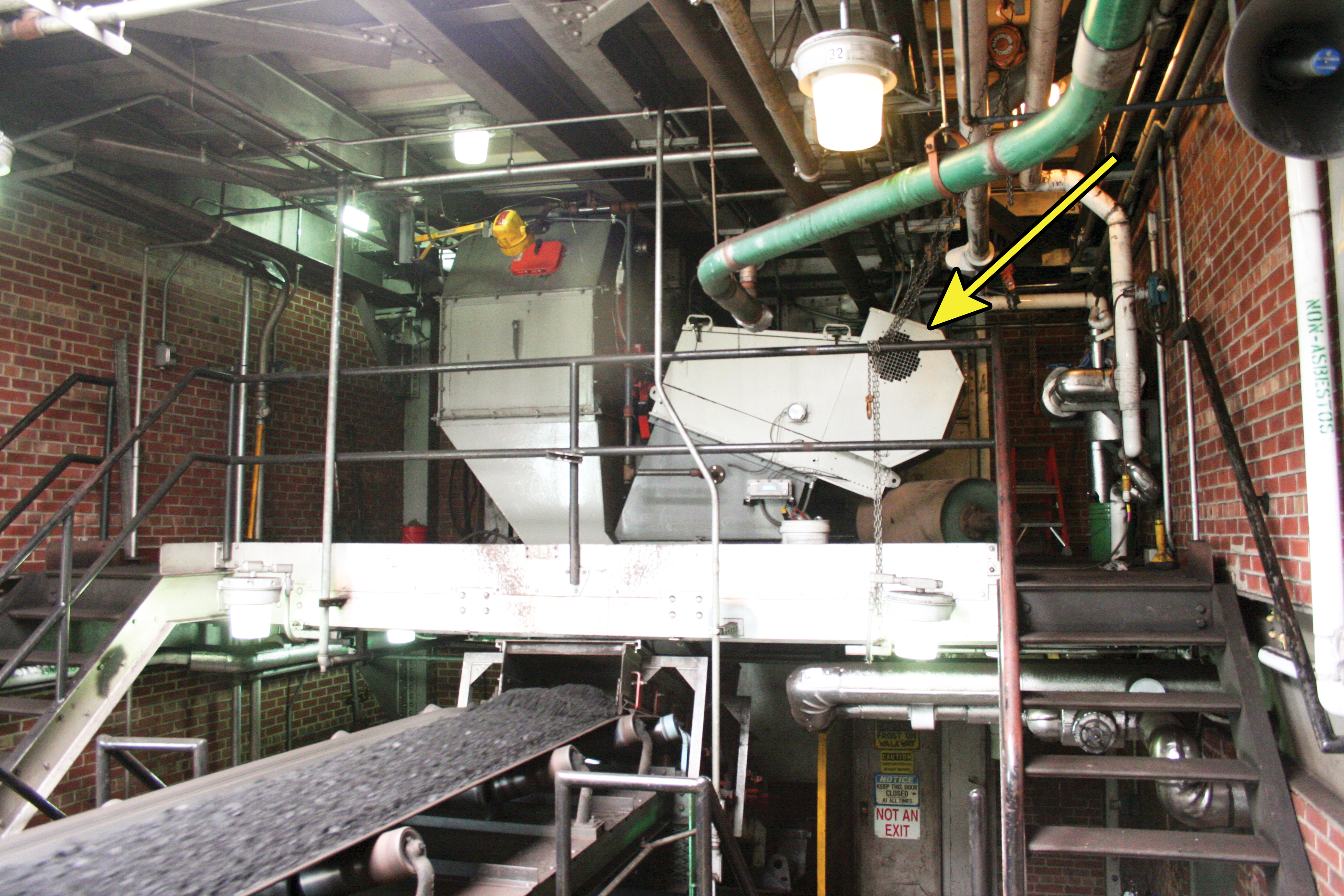
Insertable dust collectors control contamination at its source. Installed above transfer points or other dust sources, they are small and self-contained, consisting of a fan and some form of dust filter. These collectors can use the positive pressure of the conveyor air, or they can be fan powered. The systems are designed to allow the filter bags or cartridges to be arranged vertically, horizontally, or at any angle. Insertable collectors eliminate ducting, reducing installation costs as well as energy costs during operation. They are suitable for individual, isolated, or portable dust-producing operations, such as bins, silos, transfer points, or mobile conveyors.
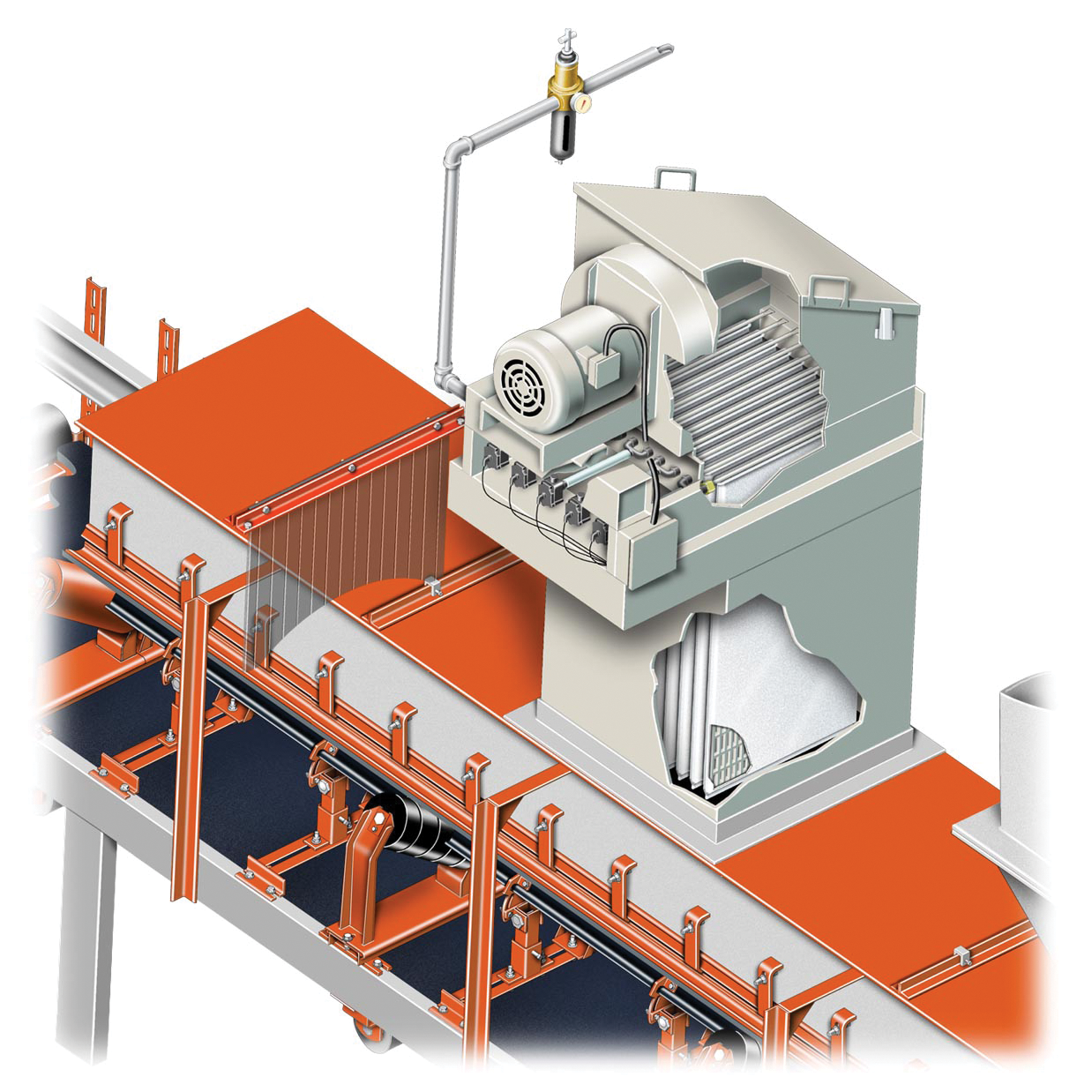
A principal advantage of this system is the elimination of ductwork. The insertable system is often more economical than centralized or unit systems, unless there are many points in close proximity that require dust control. As the static pressure is much lower, and there are no losses in pressure due to the ductwork, the fan motor is normally smaller than with other systems. The insertable system will operate only when needed—when the piece of equipment it is installed upon is running—reducing energy requirements. The dust is returned to the process at the point of generation, so there is no need for a separate dust-handling and disposal system.

Drawbacks to the insertable system include the use of compressed air to clean the filter. The compressed-air systems at many plants are already operating at a capacity, so addition of the system-standard reverse-jet cleaning system may overtax the plant air system. In addition, the use of compressed air to return dust to its source can cause a puff of airborne dust to escape from the system’s entry and/or exit areas.




















Leave Comment